Dynamic Graph
Dynamic graph in BMF is a feature to allow nodes in the graph to be added/removed/configured at the running time almost without performance penalty and block other running nodes. That means the graph built at the beginning can be changed on the fly as below:
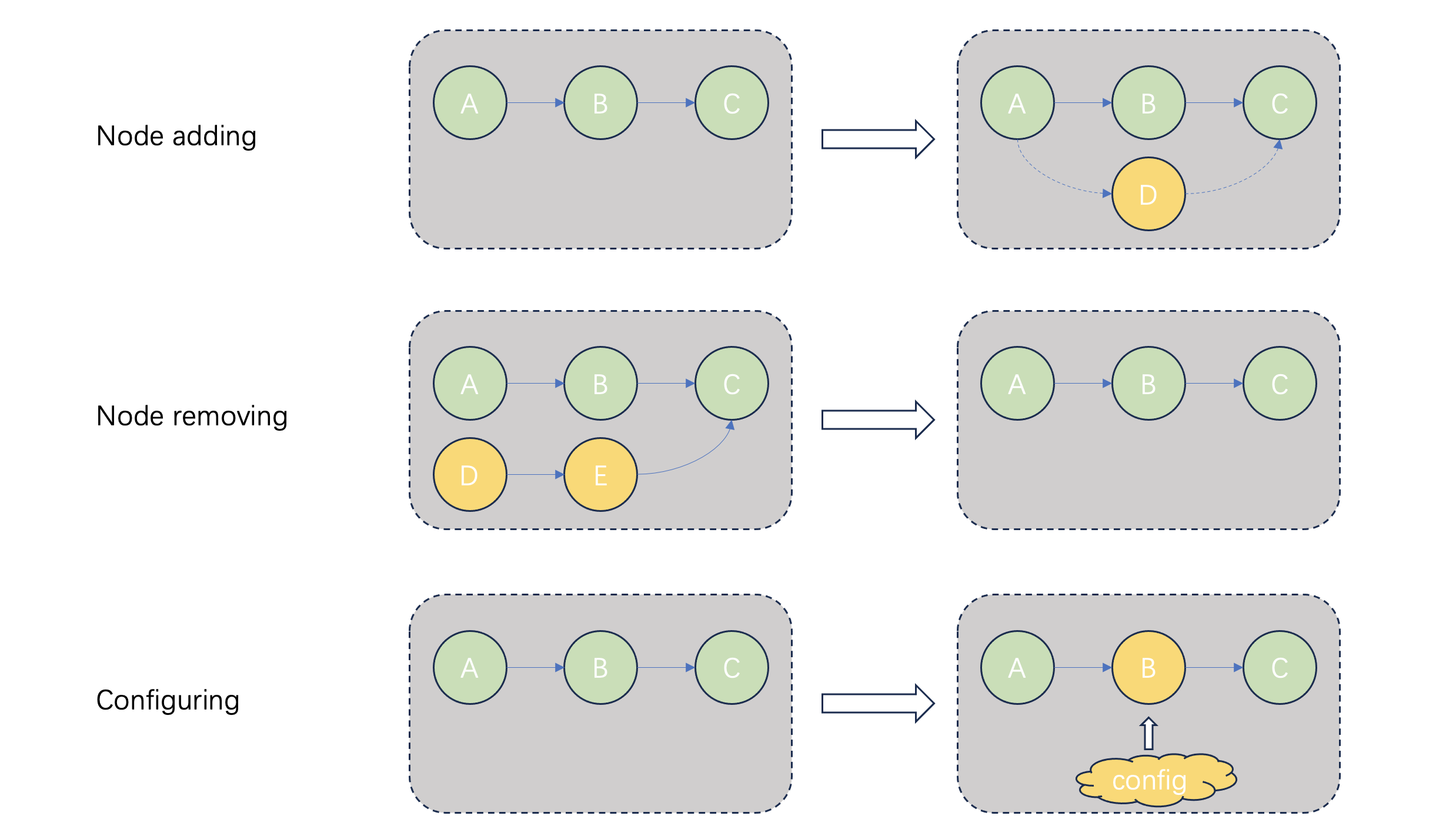
The demo and test based dynamic graph can be found in bmf/demo/broadcaster/, bmf/test/dynamical_graph/.
Related interfaces:
dynamic_add()
dynamic_remove()
dynamic_reset()
update()
run_wo_block()
Example program: \ref dynamical_graph.py
Dynamic increase:
main_graph = bmf.graph()
video1 = main_graph.decode({'input_path': input_video_path, 'alias': "decoder0"})
passthru = bmf.module([video1['video'], video1['audio']], 'pass_through',
{
'alias': "pass_through",
},
"", "", "immediate")
passthru. run_wo_block()
main_graph is used as the initially created graph, and an “alias” tag is added to each module in the graph for subsequent dynamic increase of associated usage.
When the initial graph is running, you can use run_wo_block() as a non-blocking call, or you can use run() to block the call, but you need to start another thread to support dynamic operations.
update_decoder = bmf.graph()
video2 = update_decoder.decode(
{
'input_path': input_video_path2,
'alias': "decoder1"
})
outputs = {'alias': 'pass_through', 'streams': 2}
update_decoder.dynamic_add(video2, None, outputs)
main_graph. update(update_decoder)
Dynamically adding nodes needs to specify the input stream, output stream and its own configuration to be added, and finally use the update() interface to perform actual operations.
Dynamic deletion:
remove_graph = bmf.graph()
remove_graph.dynamic_remove({'alias': 'decoder1'})
main_graph. update(remove_graph)
Dynamic deletion only needs to specify the alias of the node to be deleted.
Dynamic configuration:
main_graph. update(remove_graph)
option = {
'alias': 'encode1',
'output_path': output_path,
'video_params': {
'codec': 'h264',
'width': 320,
'height': 240,
'crf': 23,
'preset': 'veryfast'
}
}
reset_graph = bmf.graph()
reset_graph. dynamic_reset(option)
main_graph. update(reset_graph)
Dynamic configuration only needs to write the node alias and specific parameters to be configured as variables in json format as parameters of dynamic_reset().
Callback method:
Some application scenarios need to decide when to dynamically add, delete, and configure in certain module nodes. In this case, the callback mechanism of BMF can be used to cooperate. For details, see test_dynamical_graph_cb() of the example program.