Data Convert Backend
BMF Data Convert Backend
Background
An all-in-one solution is needed when multiple dimension factors are involved in video process pipeline such as CPU/GPU devices, YUV420/NV12 or RGB24/RGB48, and AVFrame or Torch structure.
As a framework, each module just focuses on its own target and data requirement, but it becomes complex when multiple modules work together as seen below in the super resolution pipeline:
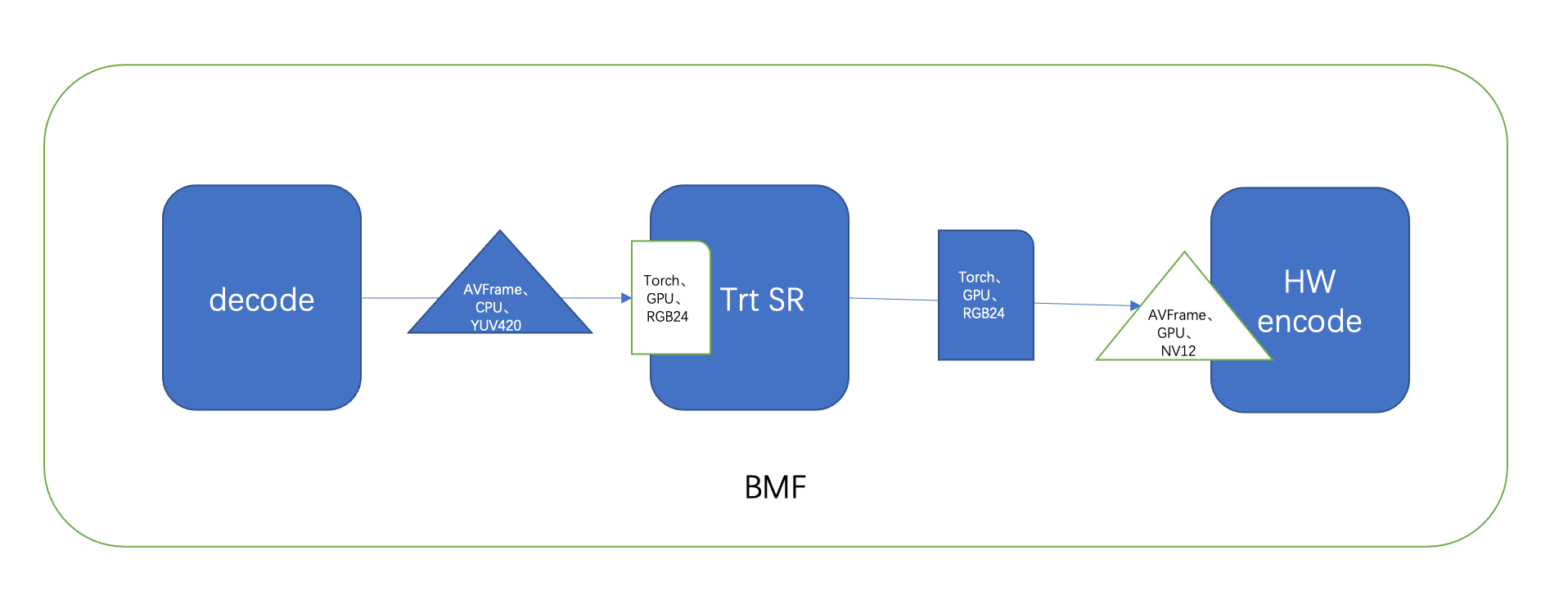
We can see that different modules have their own data requirements. The decode module outputs FFmpeg AVFrame in YUV420 pixel format, which is located on the CPU memory. The Trt SR module requires that the input data is an RGB24 torch after hardware acceleration and is located on the GPU memory. For SR through the Trt module, the output data needs to be encoded by the GPU, so the HW encode module can get AVFrame with NV12 pixel format located on the GPU memory and encode it by the GPU.
It tends to include the capabilities of video data conversion below:
- pixel format and color space
- devices between CPU and GPU
- different media types such as avframe, cvmat and torch
C++ Interface
/** @addtogroup bmf_backend_convert
* @{
* @arg src_vf: src VideoFrame
* @arg src_dp: src MediaDesc that describe src_vf's attributes
* @arg dst_dp: The desired MediaDesc of the converted VideoFrame.
* @} */
BMF_API VideoFrame bmf_convert(VideoFrame& src_vf, const MediaDesc &src_dp, const MediaDesc &dst_dp);
This interface allows the conversion of a source VideoFrame to a destination VideoFrame. If the media_type in the source MediaDesc is different from the media_type in the destination MediaDesc, it indicates that the conversion will involve the transformation between VideoFrame and a third-party data structure. Accessing a third-party data structure requires the use of the private_attach and private_get methods of the VideoFrame.
VideoFrame scale and colorspace conversion
Using bmf_convert for scale and csc:
MediaDesc dp;
dp.width(1920).pixel_format(hmp::PF_YUV420P);
auto rgbformat = hmp::PixelInfo(hmp::PF_RGB24);
auto src_vf = VideoFrame::make(640, 320, rgbformat);
auto dst_vf = bmf_convert(src_vf, MediaDesc{}, dp);
EXPECT_EQ(dst_vf.width(), 1920);
EXPECT_EQ(dst_vf.height(), 960);
EXPECT_EQ(dst_vf.frame().format(), hmp::PF_YUV420P);
Device memory transfer
The following code sample shows how to transfer the input video frame memory to GPU memory:
MediaDesc dp;
dp.device(hmp::Device("gpu")); // or hmp::Device("cpu")
auto dst_vf = bmf_convert(src_vf, MediaDesc{}, dp);
Conversion between VideoFrame and third-party data structure
BMF supports the following types of third-party structure conversion with VideoFrame
- FFmpeg AVFrame
- Opencv cv::Mat
- libtorch at::Tensor
Here, FFmpeg AVFrame is used as an example to illustrate the conversion. Other types of conversions can be referred to in the test_convert_backend.cpp.
VideoFrame to ffmpeg AVFrame
- include <bmf/sdk/av_convertor.h>, this will register AVConvertor for AVFrame
- dst_dp set media_type with value MediaType::kAVFrame
- do
bmf_convert, check if the return VideoFrame is a valid VideoFrame - use
private_get<AVFrame>to get the AVFrame pointer from the return VideoFrame.
It is important to note that the lifecycle of the structure pointed to by the pointer obtained from private_get is managed by the VideoFrame to which it belongs.
See example code snippet:
#include <bmf/sdk/av_convertor.h>
MediaDesc dp;
dp.width(1920).height(1080).pixel_format(hmp::PF_RGB24).media_type(MediaType::kAVFrame);
auto yuvformat = hmp::PixelInfo(hmp::PF_YUV420P);
auto src_vf = VideoFrame::make(640, 320, yuvformat);
auto dst_vf = bmf_convert(src_vf, MediaDesc{}, dp);
EXPECT_TRUE(static_cast<bool>(dst_vf));
const AVFrame* frame = dst_vf.private_get<AVFrame>();
EXPECT_EQ(frame->width, 1920);
EXPECT_EQ(frame->height, 1080);
EXPECT_EQ(frame->format, AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24);
AVFrame to VideoFrame
- use
private_attachset AVFrame as private_data of VideoFrame - src_dp set media_type with value MediaType::kAVFrame
- use
bmf_convertto convert - get the return VideoFrame
See example code snippet:
VideoFrame src_with_avf;
src_with_avf.private_attach<AVFrame>(frame);
MediaDesc src_dp;
src_dp.pixel_format(hmp::PF_RGB24).media_type(MediaType::kAVFrame);
VideoFrame vf = bmf_convert(src_with_avf, src_dp, MediaDesc{});
Python Interface
Data conversion is available in Python via pybind11 binding to the bmf_convert C++ implementation.
from bmf import *
Alternatively, import the specific classes/methods:
from bmf import MediaDesc, MediaType, bmf_convert
Scale and colorspace conversion
The following snippet shows a colorspace conversion from RGB to NV12 and scale conversion to half-width and half-height:
from bmf import *
# construct a video frame
width = 640
height = 360
RGB = mp.PixelInfo(mp.PixelFormat.kPF_RGB24, mp.ColorSpace.kCS_BT709)
vf = VideoFrame(width, height, pix_info=RGB)
# generate a media description of the desired converted media
dst_md = MediaDesc().width(width//2).height(height//2)
dst_md.pixel_format(mp.PixelFormat.kPF_NV12).color_space(mp.ColorSpace.kCS_BT470BG)
# do the conversion
out_vf = bmf_convert(src_vf, MediaDesc(), dst_md)
Legacy conversion functions are also available in the BMF Python module (rotate currently not supported by bmf_convert interface).
bmf.hml.hmp.img.rgb_to_yuv
bmf.hml.hmp.img.yuv_to_rgb
bmf.hml.hmp.img.yuv_to_yuv
bmf.hml.hmp.img.resize
bmf.hml.hmp.img.rotate
The following snippet uses the legacy conversion function to achieve the same conversion shown previously:
from bmf import *
# construct a video frame
width = 640
height = 360
RGB = mp.PixelInfo(mp.PixelFormat.kPF_RGB24, mp.ColorSpace.kCS_BT709, mp.ColorRange.kCR_MPEG)
vf = VideoFrame(width, height, pix_info=RGB)
# construct output pixel info and output frame
NV12 = mp.PixelInfo(mp.PixelFormat.kPF_NV12, mp.ColorSpace.kCS_BT470BG, mp.ColorRange.kCR_MPEG)
out_vf = VideoFrame(vf.frame().width(), vf.frame().height(), pix_info=NV12)
# do the conversion
mp.img.rgb_to_yuv(out_vf.frame().data(), vf.frame().plane(0), NV12, mp.kNHWC)
Device memory transfer
Using bmf_convert:
cpu_vf = pk.get(VideoFrame)
dst_md = MediaDesc().device(mp.Device('cuda:0'))
gpu_vf = bmf_convert(cpu_vf, MediaDesc(), dst_md)
#...
Or using the legacy approach:
VideoFrame.frame().device() gets the Device property
VideoFrame.cuda() moves the memory data on cuda memory
VideoFrame.cpu() moves the memory data on cpu memory
Sample code:
from bmf import *
import bmf.hml.hmp as mp
vf = pkt.get(VideoFrame)
if (vf.frame().device() == mp.Device('cpu')):
vf = vf.cuda()
#...
Conversion between VideoFrame and third-party data structure
The general class of video frame in BMF is VideoFrame, and contains Frame as a member. The python API supports conversion between VideoFrame and the following third-party data types:
- numpy
- torch
NOTE: conversions must be to-or-from a BMF Video Frame or a runtime error will be raised.
bmf.hml.hmp.Frame.numpy converts a BMF Frame to numpy, and Frame can be included in VideoFrame
bmf.hml.hmp.Frame.from_numpy
Sample code:
from bmf import *
import numpy as np
npa = np.array(obj)
rgb = mp.PixelInfo(mp.kPF_RGB24)
frame = mp.Frame(mp.from_numpy(npa, rgb))
vf = VideoFrame(frame)
#...video frame process
np0 = vf.frame().plane(0).numpy()
np1 = vf.frame().plane(1).numpy()
np2 = vf.frame().plane(2).numpy()
For bellow interface, Torch Enabled BMF is needed by compile, please reference “Install” section.
bmf.hml.hmp.from_torch convert a torch into bmf Frame
bmf.hml.hmp.torch convert bmf Frame to torch
Sample code:
from bmf import *
import torch
vf = pkt.get(VideoFrame)
torch_data = vf.frame().data().torch()
#...torch process
from bmf import *
import bmf.hml.hmp as mp
import torch
vf = pkt.get(VideoFrame)
rgb = mp.PixelInfo(mp.kPF_RGB24)
torch_vf = torch.from_dlpack(vf.reformat(rgb).frame().plane(0))
#... process of torch
RGB = mp.PixelInfo(mp.PixelFormat.kPF_RGB24, mp.ColorSpace.kCS_BT709, mp.ColorRange.kCR_MPEG)
frame = mp.Frame(mp.from_torch(torch_vf.contiguous()), RGB)
bmf_vframe = VideoFrame(frame)
#...
Underlying data type conversion
Conversion of the underlying data type of the BMF Video Frame is also possible using bmf_convert similar to the C++ examples above. The media_type property on the MediaDesc instance is used to identify the underlying data type when doing conversions with bmf_convert. The following options are available:
bmf.lib._bmf.sdk.kBMFVideoFrame - BMF video frame
bmf.lib._bmf.sdk.kAVFrame - ffmpeg AVFrame
bmf.lib._bmf.sdk.kATTensor - torch
bmf.lib._bmf.sdk.kTensor
bmf.lib._bmf.sdk.kCVMat - opencv mat
Convert ffmpeg AVFrame to BMF Video Frame:
from bmf import *
from bmf.lib._bmf.sdk import kAVFrame
vf = pkt.get(VideoFrame) # grab input AVFrame
src_md = MediaDesc().media_type(kAVFrame)
out_vf = bmf_convert(vf, src_md, MediaDesc())
#...VideoFrame process